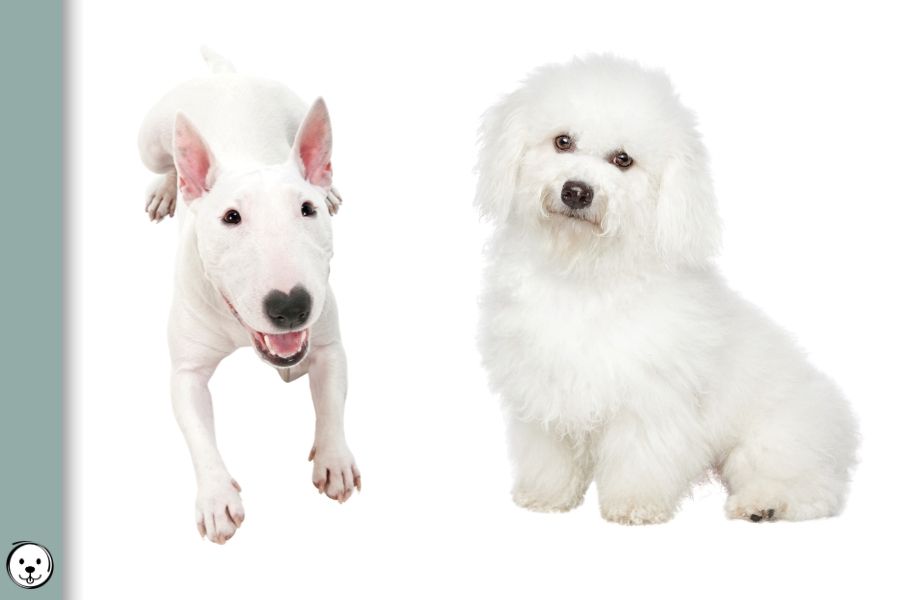
Black Fawn
Dogs with a black-based sable pattern have a predominantly tan coat with some amount of black-tipped hairs along their upper body. Their sabling can be sparse or heavy. Sable Colors Dogs need to be able to express their sable allele (we shortened the new allele names ASIPDY and ASIPSY to Ay). They have to be ky/ky combined with either a mask Em/- or a wild type allele E/-. … Read more